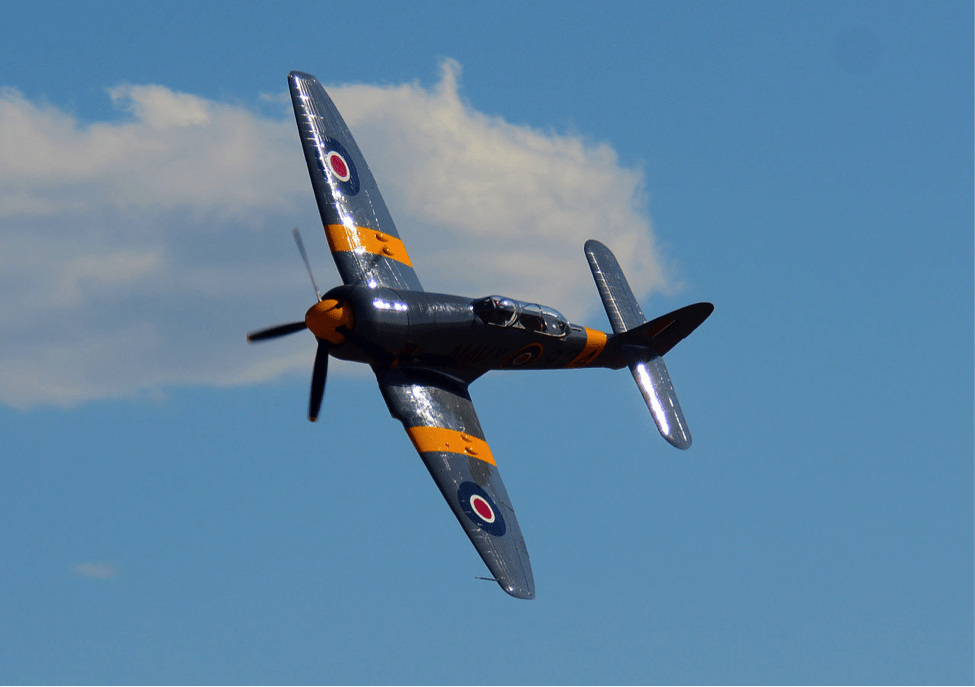
One of Today’s Most Popular Warbirds Is Also One of the Few Prop Fighters to Shoot Down a Jet.
On 21 February 1945, the prototype Hawker Sea Fury flew for the first time. The aircraft was designed by legendary British designer Sydney Camm and manufactured by Hawker for the Royal Navy, but began as an effort to produce an improved version of the earlier Hawker Tempest design for the Royal Air Force.
Although highly successful as a fighter-bomber, the Tempest was considered oversized and overweight for a pure fighter aircraft. The resulting design, first referred to as a Tempest Light Fighter, incorporated many of the Tempest’s characteristics but was smaller, lighter, and considerably faster.

Resurrected to Replace a Legend
As World War II drew to a close, the RAF cancelled its order for the aircraft. However, the Royal Navy saw the design as a suitable carrier aircraft able to replace several of its older, less capable Fleet Air Arm aircraft. Aircraft to be replaced by the Sea Fury included the Supermarine Seafire, a development of the legendary Royal Air Force Spitfire and a great fighter in its own right, but because of its narrow landing gear track and lack of pilot visibility during carrier landings, it was not considered a truly carrier-suitable aircraft.
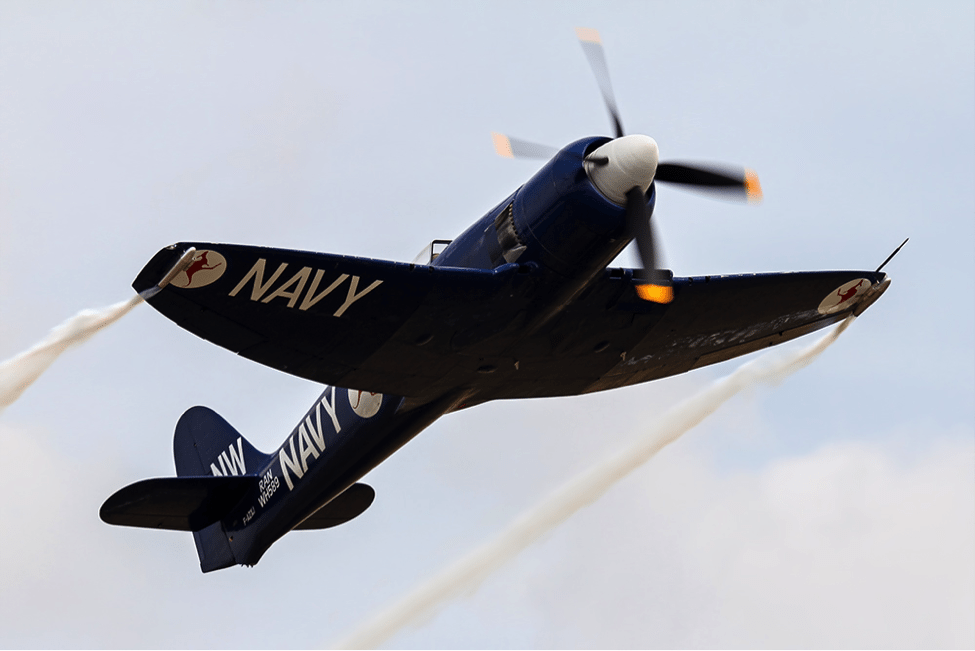
Getting Into the Blue
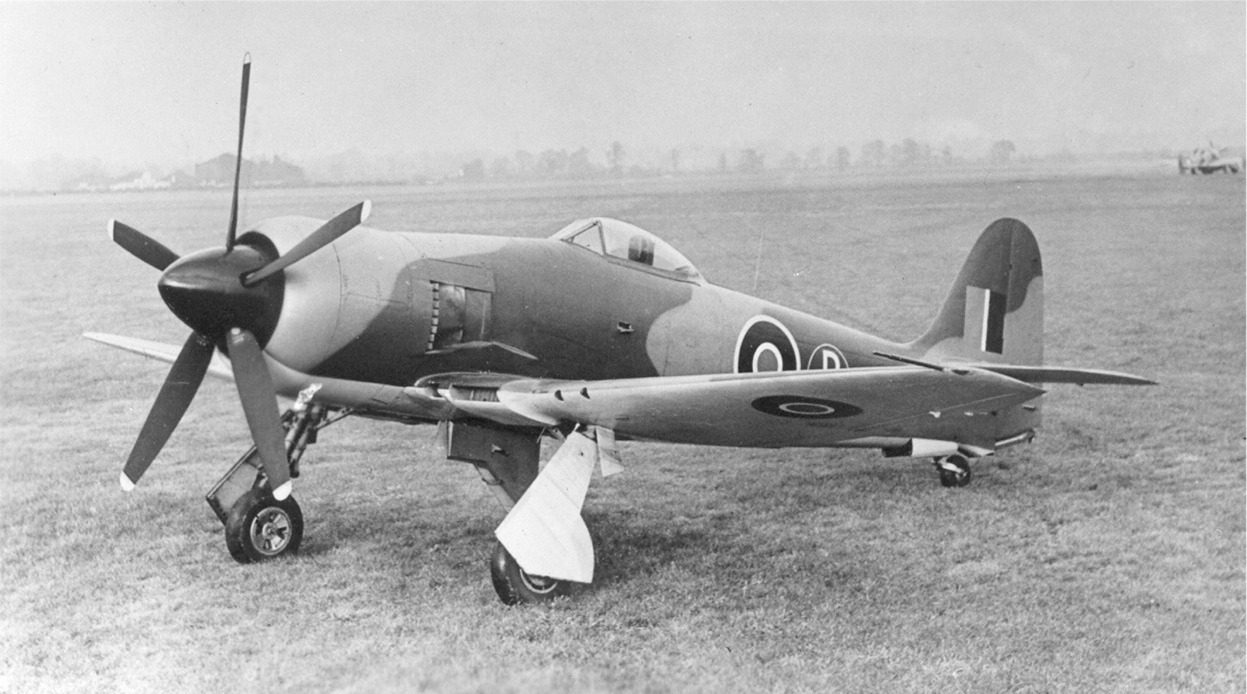
The first Sea Fury prototype, SR661, first flew at Langley, Berkshire, on 21 February 1945, powered by a 2.450 horsepower Bristol Centaurus XII engine turning a five-bladed Rotol propeller. SR661 had a tail hook for arrested carrier landings, but was not equipped with folding wings required for storage aboard aircraft carriers.
The first production model of the Sea Fury, the Sea Fury Fighter Mark 10, flew in September 1946. Carrier suitability trials aboard the aircraft carrier HMS Victorious revealed several undesirable tendencies that were quickly corrected during subsequent development. After successful completion of weapons trials at the RAF Aeroplane & Armament Experimental Establishment (A&AEE) at Royal Air Force Station Boscombe Down, the Sea Fury was cleared for operational use on 31 July 1947.

Building a Better Beast
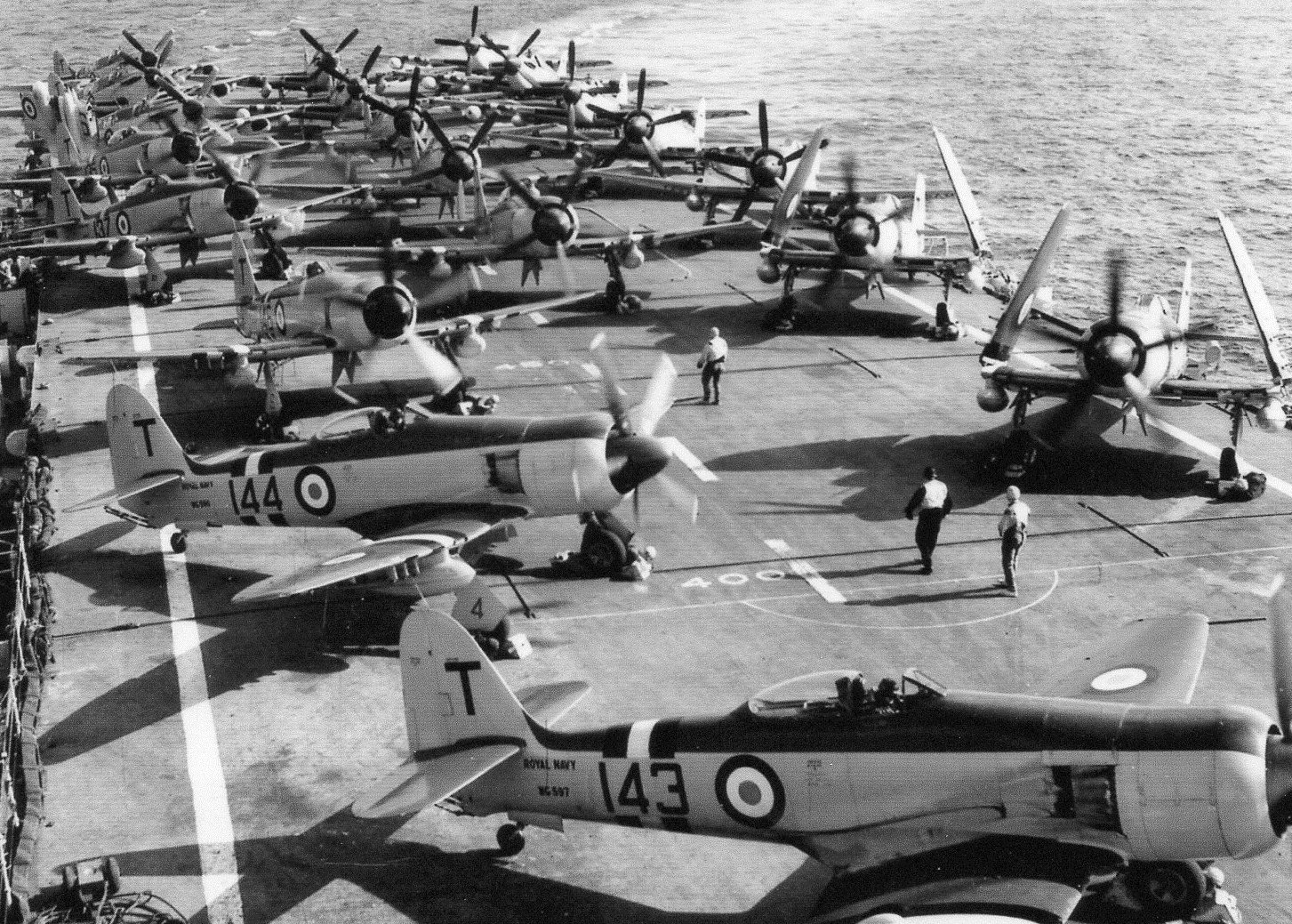
Hawker Aircraft’s effort to develop and refine the Sea Fury Mk X resulted in the more capable Sea Fury FB.11, which was equipped with folding wings. The two-seat Sea Fury T20 was also developed from the FB.11. The Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm purchased a total of 615 Sea Furies, the majority of which were the FB.11 type. Total Sea Fury production was 864 airframes of all types.

A True Fighter-Bomber
Although the Sea Fury had been originally developed as a pure air superiority fighter, the Royal Navy considered the aircraft suitable for ground attack as well. Hawker tested and cleared the type to carry and employ a wide range of armaments, including up to 16 rockets, a combination of 500 or 1000-pound bombs, mines, and drop tanks. The Sea Fury also mounted four 20 millimeter Hispano V cannon in its wings. For photo reconnaissance work, the aircraft could be fitted with both vertical and oblique cameras.
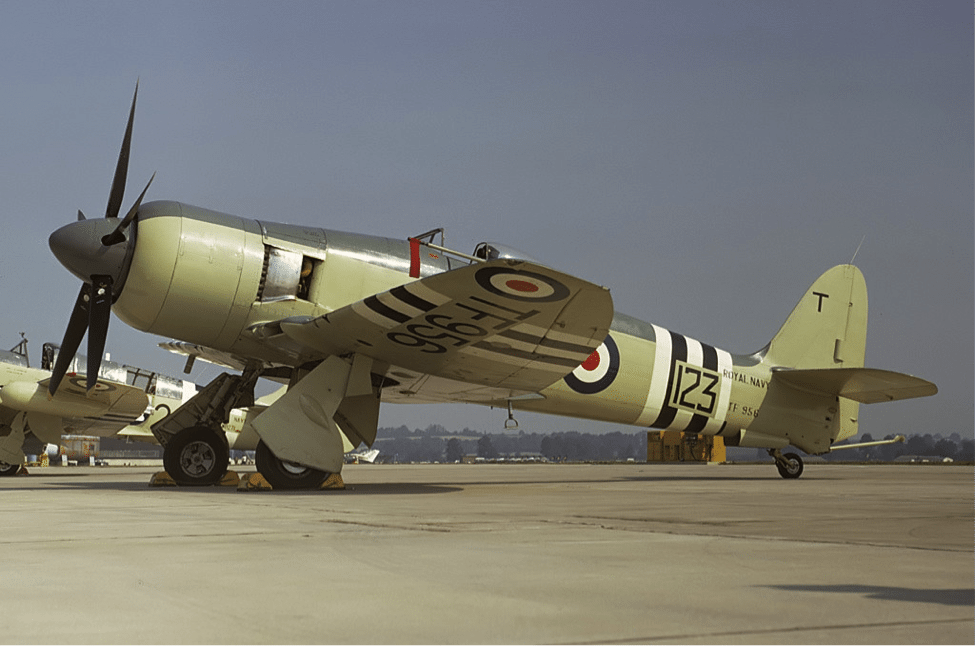
Canadians First to Fly Sea Furies
Fleet Air Arm 778 Squadron (Intensive Flying Development Unit) received the first production Sea Furies in February 1947. In May of 1947, 787 Squadron (Naval Air Fighting Development Squadron) began its development work, putting the Sea Fury to the test. The first operational unit to be equipped with the Sea Fury was Royal Canadian Navy 803 Squadron, which replaced their Seafires with Sea Furies in August 1947. In September of 1947, 807 Squadron became the first operational Royal Navy Sea Fury squadron.
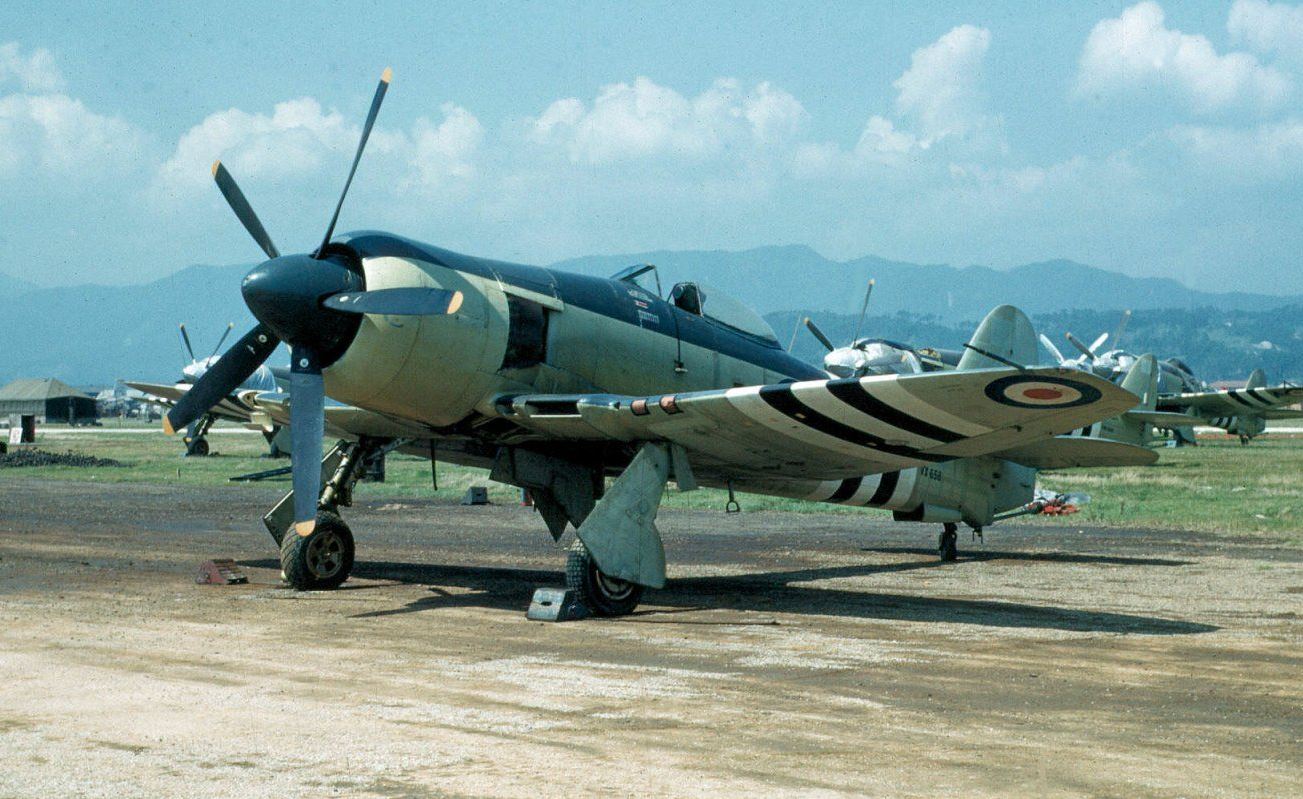

To Sea With the Brits
The Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve (RNVR) began operating Sea Fury FB.11s in August 1951. RNVR units also operated the Sea Fury T.20 two-seat trainer version of the Sea Fury beginning in late 1950. Reserve pilots were able to gain experience in the Sea Fury flying the T.20 before trading their Supermarine Seafires for Sea Fury FB 11s. RNVR 1831, 1832, 1833, 1834, 1835, and 1836 Squadrons were all equipped with Sea Furies. Based at RAF Station Benson, RNVR 1832 Squadron was the final Fleet Air Arm Sea Fury-equipped unit and switched over to the jet-powered Supermarine Attacker in 1955.

An International Success
Australia, Burma, Canada, Cuba, Egypt, West Germany, Iraq, and Pakistan all operated the Sea Fury- some well into the 1960s. Operators without the requirement for aircraft carrier operations simply removed the tail hooks and catapult bridle mounts from the aircraft. Cuban pilots successfully employed their Sea Furies against the invaders at the Bay of Pigs in 1961.